Oil India Limited
Key Initiatives: Reduction of Energy Consumption and Emissions
Renewable Energy Expansion (5-5.5 GW by 2040)
- Partnerships for Decarbonization: MoU with NTPC for collaboration in renewable energy, green hydrogen, geothermal energy, and carbon sequestration.
- Installed Renewable Capacity (188.1 MW):
- Wind (174.1 MW) and Solar (14 MW) projects operational.
- Supporting ‘One Sun-One World-One Grid’ initiative.
- Rooftop solar plants in new buildings and captive solar for internal processes.
- Collaborations for Large-Scale Solar Projects:
- Assam (645 MW): JV with APDCL, starting with a 25 MW solar project in Namrup. Himachal Pradesh (150 MW): Expanding renewable infrastructure in new regions.
Energy-Efficient Infrastructure
- Gas Engine Generator (GEG) Plant (3×10 MW) with advanced features:
- Continuous Emission Monitoring to track and control air pollution.
- Real-time gas analysis & auto-tuning for optimized combustion efficiency.
- Automated power distribution & load shedding for stable operations.
- Gas leakage & fire monitoring system for enhanced safety.
Carbon Capture & Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR)
- CO2 Injection Study (Kathaloni Crude, Assam):
- Research using Slim Tube Apparatus to determine Minimum Miscibility Pressure (MMP) for CO2-enhanced oil recovery.
- Collaboration with University of Calgary, IIT-Kharagpur, IIT-Guwahati, and others.
Climate Adaptation, Resilience, and Transition
Climate Challenges & Need for Resilience
- Climate change is causing rising temperatures, irregular precipitation, extreme weather events, and sea-level rise.
- The oil & gas sector must address its environmental impact while transitioning toward a low-carbon economy.
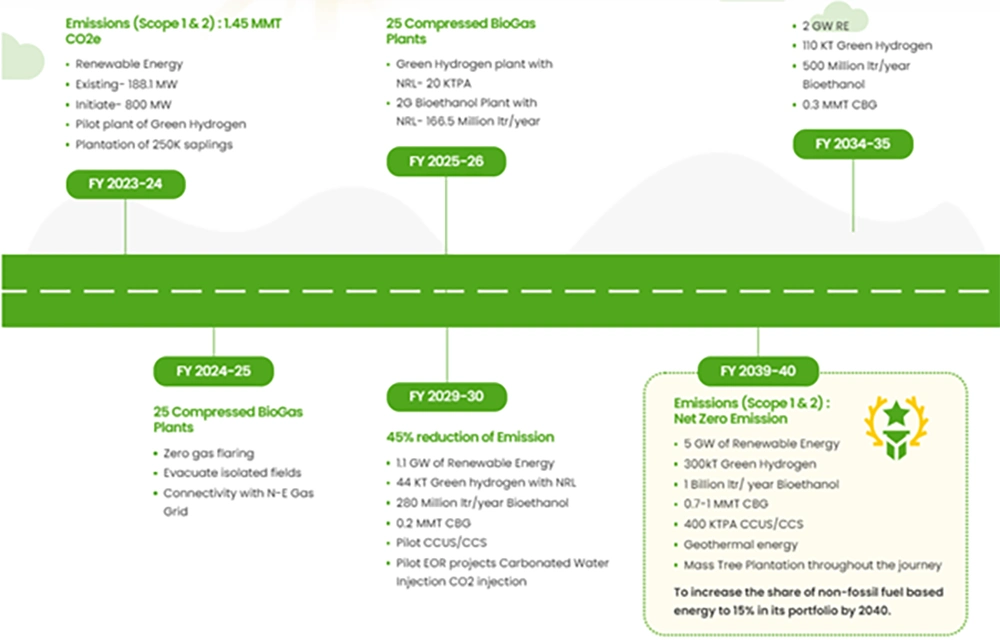
OIL’s Net-Zero Strategy by 2040
- OIL is committed to achieving Net-Zero emissions (Scope 1 & 2) by 2040 through cleaner energy adoption, renewables, and emissions reduction technologies. Investment of INR 25,000 Cr is planned to support this transition.
- Expansion of natural gas infrastructure to increase production from 3 BCM to 5 BCM by 2030.
- Green Hydrogen Development:
- 100 kW pilot plant at Jorhat (Assam), powered by 500 kWp solar plant.
- Hydrogen fuel cell e-bus project under “SNEH” initiative.
- 2.2 KTPA green hydrogen plant under construction, expected by June 2025.
- Biofuel Projects:
- Establishing 25 compressed biogas (CBG) plants under the SATAT scheme.
- Bioethanol Plant (50 KTPA) in Assam using bamboo as feedstock, aligned with India’s 20% ethanol blending target.
Carbon Capture, Utilization & Storage (CCUS)
- CCUS in Assam: Collaboration with the University of Houston for CO2 injection in Naharkatiya Field (implementation by 2027).
- CCUS in Rajasthan: Pre-feasibility study for CO2 storage in the Jaisalmer Basin.
- Afforestation under Project Vasundhara:
- 250,000 saplings planted in Digboi (Assam).
- 78,000 saplings at abandoned well sites, sequestering 507 tons of CO2.
- 1,250 hectares of voluntary plantations under the Green Credit Program in Assam, Rajasthan, and Odisha.
Short-Lived Climate Pollutants (SLCPs) like methane, black carbon, and VOCs are being monitored and reduced in alignment with the Paris Agreement’s 1.5°C goal.
- Rigorous air quality monitoring at operational sites, adhering to CPCB and MoEFCC guidelines.
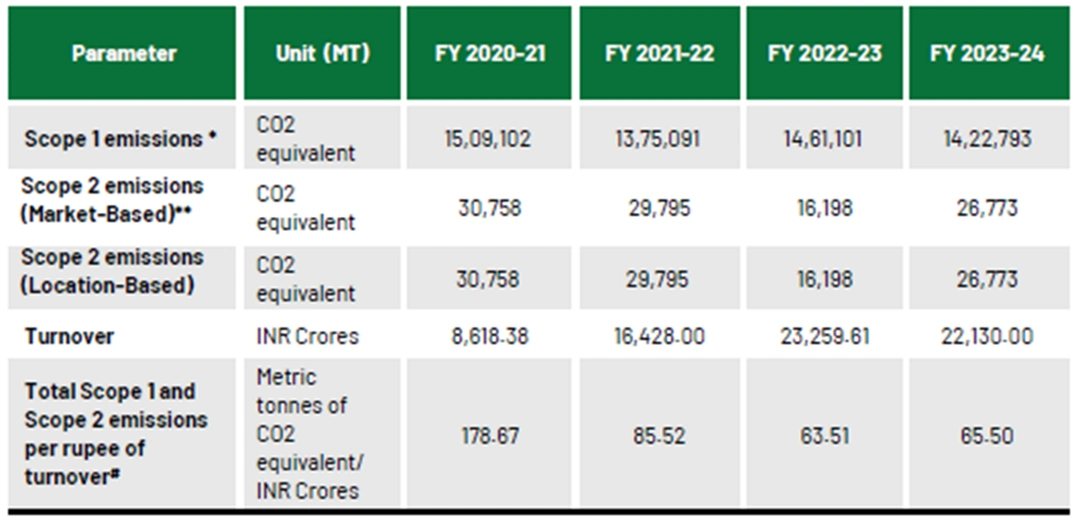
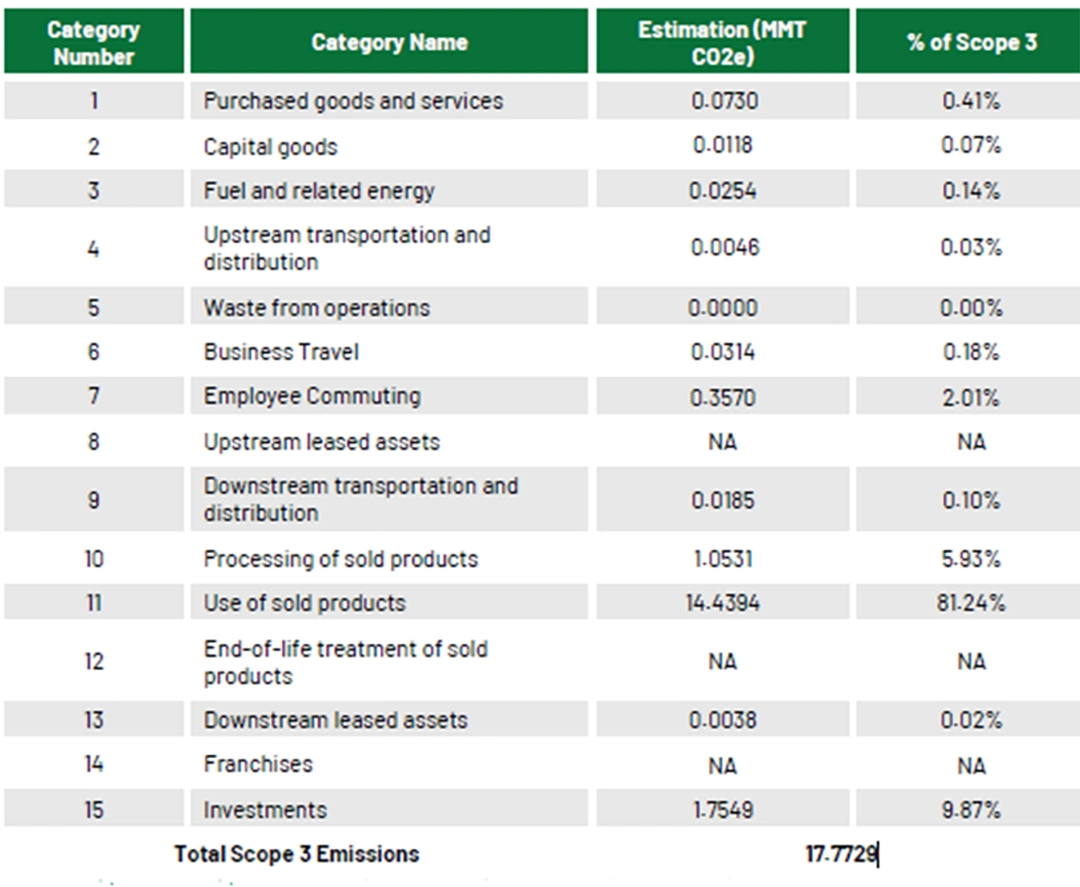
Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions & Transparency
- OIL ensures transparent emission reporting with detailed methodologies for quantification.
Water Resource Management
- Freshwater Reduction: Water withdrawal decreased from 15.57 million cubic meters (FY 22-23) to 2.73 million cubic meters (FY 23-24).
- Wastewater Recycling: Investment in Effluent Treatment Plants (ETPs) with Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) compliance.
- Water Stress Mitigation: Risk assessment using WRI’s Aqueduct tool and implementation of rainwater harvesting in Rajasthan.
Efficient Waste Management
Waste Generation & Environmental Impact
- The oil & gas industry produces significant waste, including drilling muds, cuttings, oil sludge, and hazardous materials.
- Improper disposal can contaminate surface water, groundwater, and marine environments, affecting biodiversity and human health.
- OIL adheres to regulatory norms and focuses on bioremediation, recycling, and proper disposal to minimize environmental risks.
Waste Reduction & Recycling Initiatives (FY 2023-24)
- Oily Sludge: 3,581.56 MT generated, with 2,456.13 MT bioremediated and 113.75 MT of spent oil sent to recyclers.
- Plastic Waste: 32.83 MT managed.
- E-waste: Reduced from 16.68 MT (FY 22-23) to 12.92 MT (FY 23-24).
- Battery Waste: Increased from 15.91 MT to 52.57 MT.
- Drill Cuttings: 378.54 MT processed following MoEF&CC guidelines.
- Chemical Sludge from Wastewater Treatment: 98.44 MT treated.
Sustainable Waste Management Practices
- Bioremediation & Recycling: Used for oil sludge, reducing environmental impact.
- Effluent Treatment Compliance: All waste treated as per Pollution Control Board norms.
- Collaboration for Sludge Processing: Partnership with Balmer Lawrie & Co. Ltd. for sludge treatment.
- Reusing Workover Well Brine & Mud: Reducing chemical costs and minimizing waste.
OIL’s waste management approach aligns with its sustainability strategy, ensuring compliance, environmental responsibility, and resource efficiency. Let me know if you need further refinements!
Biodiversity Management
- Biodiversity Conservation:
- Collaborations with Assam Biodiversity Board and IUCN.
- Restoration of 26 well sites in Assam and 9 in Rajasthan for ecological preservation.
To know more, visit –
https://www.oil-india.com/sustainability/sustainability-home